Apache POI 간단 정리
Apache POI 란?
마이크로소프트 오피스 파일 포맷을 순수 자바 언어로서 읽고 쓰는 기능을 제공하는 라이브러리
프로젝트에 Apache POI 추가하는 방법
Maven
1
2
3
4
5
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3</version>
</dependency>
Gradle
1
implementation 'org.apache.poi:poi-ooxml:5.2.3'
23.09.25 기준 안정화 버전은 5.2.3 버전이며 4.0 이상을 사용하려면 Java 8 버전 이상을 사용해야 한다.
poi-ooxml 모듈을 추가하면 poi 모듈까지 함께 추가된다.
핵심 클래스
- Workbook
- 하나의 엑셀 파일을 의미한다.
- Sheet
- 엑셀의 시트를 의미한다.
- Row
- 하나의 행을 의미한다.
- Cell
- 하나의 셀을 의미한다.
핵심 클래스는 모두 인터페이스로 구현체는 HSSF* , XSSF* 등이 있다.
HSSF로 시작하는 구현체는 .xls 확장자 파일을 처리할 때 사용하고
XSSF로 시작하는 구현체는 .xlsx 확장자 파일을 처리할 때 사용한다.
엑셀 파일 Write
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
public class ExcelWrite {
public static String filePath = "./files";
public static String fileNm = "example.xlsx";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 빈 workbook 생성
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook();
// 빈 sheet 생성
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("sheet01");
// 엑셀에 쓸 데이터 생성
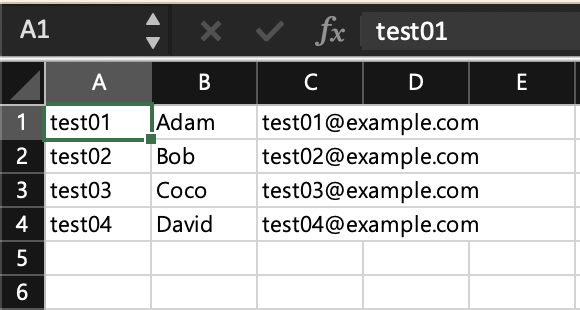
List<String[]> data = new ArrayList<>();
data.add(new String[]{"test01", "Adam", "test01@example.com"});
data.add(new String[]{"test02", "Bob", "test02@example.com"});
data.add(new String[]{"test03", "Coco", "test03@example.com"});
data.add(new String[]{"test04", "David", "test04@example.com"});
// 데이터를 순회하며 셀에 값 대입
for (int rownum = 0; rownum < data.size(); rownum++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum);
for (int cellnum = 0; cellnum < data.get(rownum).length; cellnum++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellnum);
String value = data.get(rownum)[cellnum];
cell.setCellValue(value);
}
}
// 엑셀을 저장할 디렉터리 체크
File file = new File(filePath, fileNm);
File dir = file.getParentFile();
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdir();
}
// 디렉터리에 엑셀 생성
try (FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file)) {
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
엑셀 파일 Read
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class ExcelRead {
public static String filePath = "./files";
public static String fileNm = "example.xlsx";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 파일을 읽어온다.
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(filePath, fileNm));
// 읽은 파일로 Workbook 인스턴스를 생성한다.
Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 첫번째 sheet 를 가져온다.
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 모든 row 를 순회한다.
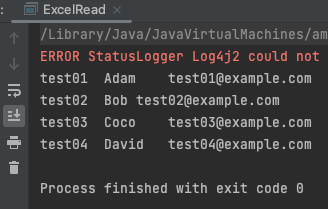
for (Row row : sheet) {
// 모든 cell 을 순회한다.
for (Cell cell : row) {
System.out.print(cell.getStringCellValue() + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
유의사항
엑셀을 읽을 때는 셀의 타입을 검사하는 것이 좋다.
셀 서식이 일반 or 텍스트 라도 셀에 숫자만 들어가있다면 Java 에서 파일을 읽을 때 Numeric 타입으로 인식되기 때문.
Numeric 타입의 셀인데 getStringCellValue() 하면 값을 가져올 수 없다고 오류가 발생한다.
1
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Cannot get a STRING value from a NUMERIC cell
셀 병합
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class ExcelWrite {
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
// 병합 예제
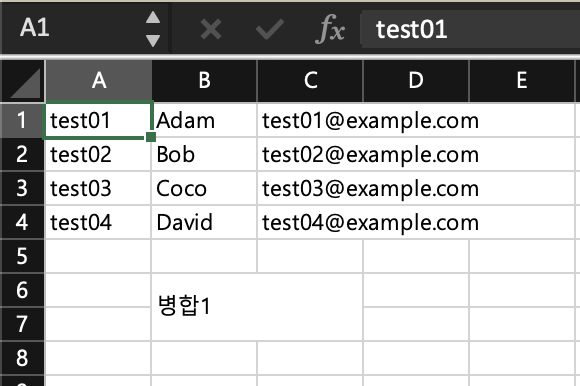
int rownum = 5;
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(rownum, 6, 1, 2)); // firstRow, lastRow, firstCol, lastCol
Row row = sheet.createRow(rownum);
Cell cell = row.createCell(1);
cell.setCellValue("병합1");
...
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.